
Revolutionizing DeFi with Coreum’s Enterprise-Grade Blockchain
The advent of blockchain technology has led to all sorts of applications that can now run on a decentralized, immutable network. Nowadays, there is almost a blockchain for every application you can think of.
With over 20,000 cryptocurrencies, more than 500 exchanges and a plethora of NFT and DeFi (decentralized finance) projects, the blockchain ecosystem is rapidly expanding, and there is seemingly no end to its expansion.
This growth has led to increased innovation and investment in space.
Many industries are already exploring using blockchain to improve their operations and provide new growth opportunities. From supply chain management to voting systems to digital identity solutions, the potential applications of blockchain technology are numerous.
However, there is a caveat. The problem of scalability, interoperability and security plagues most blockchain networks and seriously threatens to slow down a multi-billion dollar industry.
While several solutions have emerged from blockchains such as Ethereum, Polkadot, Cosmos and Solana, among others, few offer an optimal blockchain development framework for enterprise.
Coreum is the first-of-its-kind modular, fast, secure and interoperable enterprise-grade blockchain.
Here is a breakdown of how it works, but first let’s look at blockchain’s most pressing challenges.
The Need for a Robust Blockchain for DeFi
One of the main challenges plaguing the blockchain development space is interoperability.
The development of numerous blockchain networks, each with its own specific use case and capabilities, has created a fragmented ecosystem that limits the full potential of blockchain technology.
This is particularly problematic for DeFi, where interoperability is critical for creating truly decentralized financial systems operating seamlessly across different networks and platforms.
Whether you are building dApps(decentralized applications) on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Cosmos, the reality is that all these blockchains need to work together to make it easy for users to chain-hop with limited difficulty.
Projects such as Cosmos are making great progress in this regard.
While Ethereum is designed as a second-generation blockchain that enables smart contracts, Cosmos offers a new approach to blockchain interoperability, focusing on enabling communication between independent blockchain networks.
Instead of competing with Ethereum, Cosmos complements it by providing a scalable and interoperable infrastructure that can enhance the functionality of Ethereum and other blockchain networks built on top of the EVM.
This is particularly important for DeFi and enterprise-grade blockchains that require seamless communication and interoperability between different blockchain networks to create a seamless user experience.
Cosmos’ interoperability solutions are designed to enable DeFi protocols to operate across different blockchain networks, providing users with greater flexibility and choice.
For example, a DeFi protocol built on Ethereum could leverage Cosmos’ interoperability solutions to enable users to move assets seamlessly between Ethereum and other blockchain networks, such as Binance Smart Chain or Polkadot.
This removes all barriers to entry such that a user can move their digital assets from one blockchain to the other without incurring hefty fees or worrying about the loss of their digital assets as they migrate.
Simply put, Cosmos’ focus on scalability and performance makes it an ideal platform for building enterprise-grade DeFi applications that require high transaction throughput and low latency.
Cosmos, Tendermint and Coreum: Enabling an Internet of Blockchains

To enable interoperability, Cosmos utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called Tendermint, which facilitates cross-chain communication and enables decentralized applications to be built on different blockchain networks.
At its core, Tendermint is a software that contains two main parts: a consensus engine and an application interface layer. The application layer enables businesses looking to launch decentralized applications (dApps) to do so without worrying about achieving compatibility with every other chain in the DeFi world.
Given that Ethereum is the largest DeFi platform for dApp development, Cosmos (through Tendermint) enables all the blockchains built on Ethereum’s EVM to communicate and interact.
This approach allows for greater flexibility and scalability in the development and deployment of dApps, as developers can build digital assets on one blockchain and have users transact with those assets throughout the DeFi landscape.
This is why Coreum (an enterprise-grade blockchain) is built with Cosmos SDK and utilizes Tendermint’s consensus protocol to facilitate interoperability.
What is Coreum?

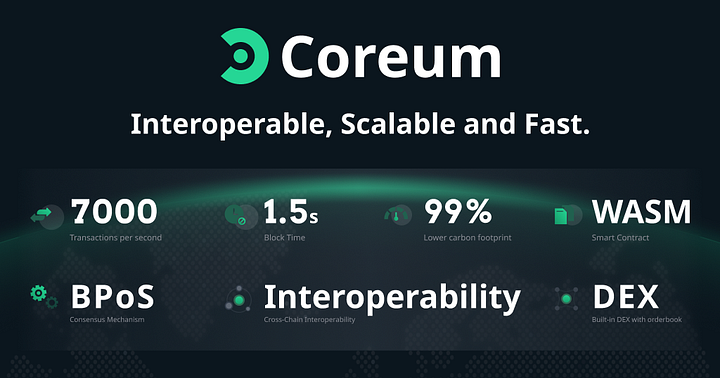
Coreum is a layer-one blockchain built to be fast, secure, interoperable and modular.
In terms of speed, Coreum stands out even when compared to top blockchain networks such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. While the transactional throughput of Bitcoin and Ethereum stands at only a few transactions per second, Coreum is designed to handle seven thousand transactions per second, making it an ideal platform for building enterprise-grade applications that require high throughput and low latency.
In addition to its speed, Coreum is also highly secure in addition to its speed, with advanced security features such as a federated validator group of nine validators who rotate every four hours. This means that the validator group is highly decentralized and not controlled by any single entity, ensuring that the network remains secure and resistant to attacks.
Moreover, Coreum utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called Bonded Proof of Stake (BPoS). Thanks to the Cosmos SDK, Coreum can leverage the power of an energy-efficient yet secure consensus protocol that allows Coreum to incentivize staking and hence boost its security.
With a much higher TPS (transaction per second) and a robust blockchain network, Validators on Coreum can earn more in terms of transactional fees, and more people will stake their tokens.
To top it all off, Coreum also features a native token called CORE which is used in staking and earning rewards in the Coreum ecosystem.
How Coreum’s Enterprise-Grade Blockchain Works
As mentioned, Coreum is designed as an enterprise-grade blockchain for solving real-world problems at scale.
Coreum uses the Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus mechanism (BFT) from Cosmos and WebAssembly to process smart contract transactions. This architecture alone facilitates speedy transactions, thus incentivising participants to conduct more transactions and access bulk fee discounts.
Businesses can launch a token system or digital asset platform on Coreum, as its purpose is to provide a foundational framework for building decentralized and interoperable dApps.
Coreum is the first-of-its-kind enterprise-grade blockchain (ECB) built to give businesses essential tools and infrastructure for building any size enterprise decentralized application.
What’s more, Coreum complies with ISO20022 regulatory requirements; therefore, businesses can leverage the benefits of blockchain technology without worrying about compliance issues.
ISO20022 is a global standard for financial messaging, ensuring interoperability and compatibility across different financial systems and institutions.
Moreover, Coreum’s modular architecture enables businesses to build custom solutions tailored to their specific needs or customers. Modularity also simplifies the process of upgrading and updating the platform well into the future.
Here is a look at the top features that Coreum offers.
Coreum Features:
Speed and scalability
Speed is necessary when trying to create decentralized applications with high transactional throughput. But, undeniably, there is an invariable limit to how much you can scale a software even if you add more resources.
That is why Coreum’s engineers opted for parallel scaling or horizontal scaling instead of vertical scaling. Therefore, Coreum comes with side chains that can double the TPS rate of Coreum from 7,000 to 14,000 transactions per second.
Granted, applications such as decentralized exchanges are not built to run on two chains. However, developers can go as far as building a dedicated mainnet as well as an extra chain for the DeX of their dApp.
Cost-efficient gas fees
Adding to Coreum’s speed and scalability is its unique fee model. Coreum has an automatic gas price adjustment mechanism that is triggered by the current transaction load throughout the network. All parameters of this fee model are governed by Coreum’s on-chain governance. This fee model is designed with a moving average that keeps the gas fees relatively low and affordable.
In fact, interacting with smart tokens and digital assets on Coreum is much cheaper than interacting with Smart Contracts. The fees are always set according to known computational parameters. Therefore, transactions do not depend on the gas offered by network users, as is the case on networks such as Ethereum. With Coreum, each transaction has a somewhat fixed gas fee unless the network is congested. A fixed gas fee enables predictable management of the network’s performance.
Staking and Rewards
Like any other Proof-of-Stake network, Coreum comes with a staking mechanism. The validators are given the work of ensuring the network operates seamlessly, and that consensus is achieved.
Therefore, anyone can become a validator by bonding a minimum of 20,000 CORE tokens using a self-delegated staking mechanism. However, staking these CORE tokens doesn’t guarantee that a validator will be part of the consensus. Thanks to the BPoS consensus protocol, only 32 validators with the highest stake can participate. This further adds to the flexibility, speed and efficiency of the network, as not all validators are required to reach a consensus.
The most active validators in the network get to split block rewards proportional to their stake, thus acting as an incentive for participation. These rewards come from transaction fees in the network as well as additional rewards generated and allocated by the Coreum blockchain.
Security
In a BPoS system such as Coreum, the security of the network is ensured not only by selecting validators with a stake in the network but also by implementing mechanisms to punish malicious behavior and ensure that validators act in the best interest of the network.
If a validator is found to have acted maliciously, such as attempting to double-spend or colluding with other validators to attack the network, they can have their bond slashed. In Coreum’s case, the slashing mechanism is directly taken from the Cosmos SDK module and involves disqualifying a validator from the committee board as punishment.
The bond-slashing mechanism is typically implemented through a smart contract that automatically penalizes validators who violate the network’s rules. When a validator is caught acting maliciously, the smart contract will trigger a slashing event, which will result in the loss of a portion or all of the validator’s bond.
The severity of the slashing penalty can vary depending on the severity of the offense. The slashing mechanism ensures that validators are held accountable for their actions and incentivizes them to act honestly and in the best interest of the network. By disincentivizing malicious behavior, BPoS systems can create a more secure and reliable network that can provide a high level of protection against attacks and manipulation.
Interoperable
Interoperability is the party piece of the Coreum network.
With a BPoS blockchain built on Cosmos SDK and Tendermint, such as Coreum, developers can achieve interoperability through the use of the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.
IBC enables communication and asset transfer between different blockchain networks. Cosmos SDK, on the other hand, offers a modular framework for building blockchain applications that are designed to be highly customizable and flexible. It enables developers to create custom blockchain applications with specific features and functionalities tailored to their needs.
Also, as mentioned earlier, Tendermint is the consensus engine that runs the Coreum blockchain network. It is designed to provide dApps on Coreum with high levels of security and scalability, making it an ideal choice for building enterprise-grade blockchain applications that are interoperable.
For instance, DEXs(decentralized exchanges) built with Coreum can leverage its IBC protocol to enable asset trading between different blockchain networks. This would enable users to trade assets on the DEX using different cryptocurrencies from different blockchain networks, providing greater liquidity and flexibility.
Moreover, the interoperability features of a BPoS blockchain built on Cosmos SDK and Tendermint can also enable cross-chain smart contracts, which can automate complex business processes across different blockchain networks. This can create new growth opportunities for businesses and organizations, enabling them to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology across multiple networks and ecosystems.
Conclusion
The future of blockchain technology is getting better as more innovative solutions emerge. Coreum is the first-of-its-kind EGB that is working to revolutionize the DeFi industry by providing a modular, fast, secure, and interoperable blockchain platform for enterprises. With its focus on speed, scalability, cost-efficient gas fees, staking and rewards, security, and interoperability, Coreum offers a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology without compromising on security, scalability, or compliance.
Coreum’s use of the Tendermint consensus protocol and the Cosmos SDK offers a unique approach to interoperability, enabling communication and asset transfer between different blockchain networks. This allows developers to build decentralized applications that can operate seamlessly across different networks and platforms, providing greater flexibility and choice for users.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to expand and evolve, the need for enterprise-grade blockchain solutions such as Coreum will only become more apparent. With its innovative approach to scalability, interoperability, and security, Coreum is poised to play a significant role in the future of DeFi and enterprise-grade blockchain applications.
About Ubik Capital
Capital is a Proof-of-Stake service provider, validator, and investor. Ubik Capital provides staking-as-a-service as well as investments to various blockchain projects. Ubik Capital secures major networks and is a trusted staking provider with years of industry experience.
We’d love to delegate to us!
Be a part of our community!
Website: https://ubik.capital/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ubikcapital
Telegram: https://t.me/ubikcapital
Discord: https://discord.gg/9Jzbk4MZPF
E-mail: contact@ubik.capital
Delegation
Ubik Capital is a PoS validator across several networks, including Solana, Cosmos Network, Polkadot, Oasis Protocol, Crypto.com, Band Protocol, Aleph Zero, ICON Network, xx Network to mention a few.
Ubik Capital makes it easy for users to stake and delegate their coins by providing them with simple guides and 24/7 support. Furthermore, with 100% uptime across all networks, users can be assured that their coins are always being staked and earning rewards.
If you’re interested in staking your coins with Ubik Capital, you can check out some of their top guides on how to do so:
- How to Stake Solana SOL with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Polkadot DOT with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Cosmos Network ATOM with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Oasis Protocol ROSE with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Crypto.com CRO with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Injective INJ with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Band Protocol BAND with Ubik Capital
- How to Stake Aleph Zero AZERO with Ubik Capital
Ubik Capital is an excellent option if you’re interested in earning rewards by staking your coins.
Disclaimer: Not financial advice. Cryptocurrency and blockchain investments are high risk, can incur substantial losses, and are not suitable for everyone. Please consult a professional before considering investment in any cryptocurrency. This article does not encourage or support any specific investments, use of applications or technology, or financial direction. This article is for informational purposes only and should be verified and validated externally for 100% accuracy.